<!-- wp:social-links --><ul class="wp-block-social-links"><!-- wp:social-link {"url":"https://gravatar.com/wwwsoftreviewcom","service":"gravatar","rel":"me"} /--></ul><!-- /wp:social-links -->
AI Meets GDPR: Navigating the Data Protection Maze
Table of Contents
Maneuvering the intersection of AI and GDPR involves addressing fundamental GDPR principles such as data minimization, purpose limitation, and transparency. AI’s reliance on large datasets presents unique challenges in maintaining compliance, especially regarding the lawful basis for data processing, transparency, and consent. Organizations must implement Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) to mitigate risks associated with high-risk data processing. Ensuring explainability in AI decision-making processes is crucial for transparency and accountability. Effective strategies incorporate privacy by design and regular audits to safeguard data subjects’ rights. Exploring these aspects further can provide deeper insights into successful compliance strategies.
Understanding AI and GDPR Basics
Understanding the intersection of AI and GDPR begins with grasping key GDPR principles such as data minimization, purpose limitation, and the requirement for a lawful basis for data processing. AI presents unique challenges in complying with these principles, particularly due to its reliance on vast datasets and complex algorithms. Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach to guarantee AI systems are designed with data protection in mind, balancing innovation with regulatory compliance.
Key GDPR Principles Affecting AI
Steering through the intersection of AI and GDPR necessitates a thorough comprehension of key data protection principles that govern the use and processing of personal data. Central to these principles is the concept of lawful processing, which mandates that any use of personal data by AI systems must be grounded in a legitimate basis such as consent, contractual necessity, or legitimate interest. This guarantees that data subjects’ rights are respected from the outset.
Transparency is another cornerstone of GDPR, requiring that individuals are clearly informed about how their data is collected, processed, and used by AI systems. This involves providing detailed privacy notices and guaranteeing that data subjects understand the purposes of data processing and their rights under the regulation.
Further, the GDPR emphasizes data minimization, which means that AI systems should only process the minimum amount of personal data necessary for their intended purpose. This principle helps in reducing the risks associated with data breaches and misuse.
Additionally, GDPR mandates conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) for high-risk processing activities typical in AI applications. DPIAs help identify and mitigate potential risks to data subjects, ensuring compliance and fostering trust in AI technologies.
Unique Challenges of AI in Data Protection
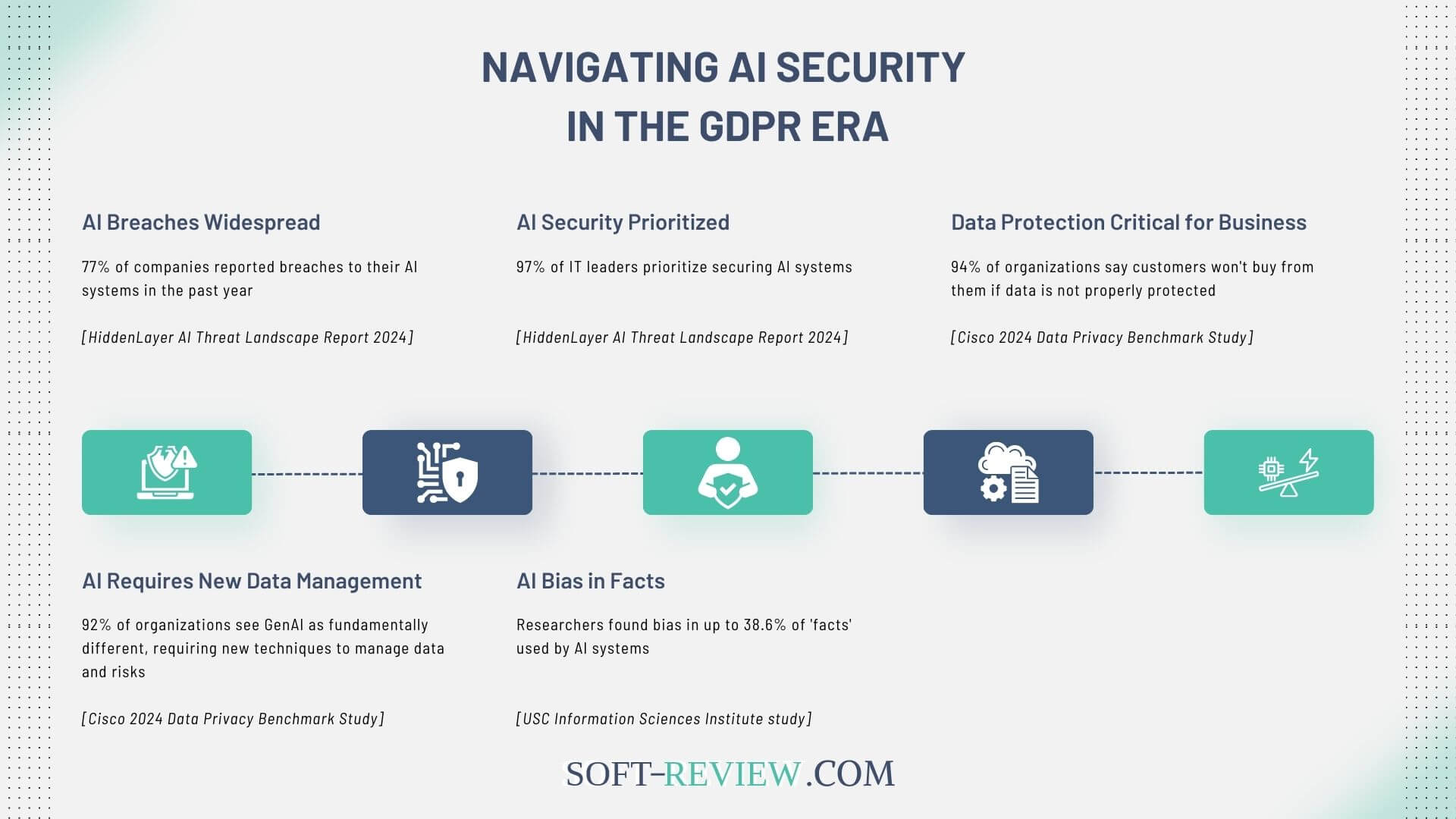
The intersection of AI and GDPR introduces complex challenges that stem from the unique nature of AI technologies and their ability to process vast amounts of data in innovative ways. One major issue is the applicability of GDPR to AI systems, especially when determining whether data used for AI training is personal data. AI’s reliance on extensive datasets complicates the classification of personal versus anonymized data, with re-identification risks requiring careful consideration.
Additionally, guaranteeing transparency in AI-driven processes poses significant difficulties. GDPR mandates clear communication about data collection and processing purposes, but AI’s complexity can obscure these details. This requires detailed privacy notices and constant updates to reflect AI’s evolving use cases.
Another challenge is managing individual rights requests, such as data deletion or correction, which become problematic once personal data is embedded in AI models. Developing strategies to address these requests, including maintaining thorough data inventories, is essential for compliance.
Automated decision-making further complicates GDPR adherence, as the regulation restricts decisions based solely on automated processing. AI developers must incorporate human oversight and document decision-making logic to mitigate risks and guarantee compliance.
For a practical overview of the key data protection considerations in generative AI development and use, the UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) has outlined eight essential questions that developers and users need to ask, covering crucial aspects from lawful basis to individual rights.
Lawful Basis for AI Data Processing
When processing personal data in AI applications under GDPR, establishing a lawful basis is paramount, with common grounds including consent and legitimate interests. Special categories of personal data, such as health information, require additional safeguards and explicit consent due to their sensitive nature. Ensuring compliance necessitates clear documentation of the lawful basis for data processing, reflecting the specific purpose and nature of the AI application.
Consent and Legitimate Interests
Establishing a lawful basis for AI data processing under GDPR often hinges on obtaining clear and informed consent or demonstrating legitimate interests. Consent requires that individuals are fully aware of what their data will be used for and explicitly agree to it. This is particularly challenging in AI applications, where data use can be complex and multifaceted. On the other hand, legitimate interests allow organizations to process data without direct consent if they can prove that their interests are not overridden by the individuals’ rights and freedoms.
| Aspect | Consent | Legitimate Interests |
|---|---|---|
| User Involvement | Requires explicit agreement from individuals | Does not require direct consent but must be justified |
| Transparency | High, with detailed information on data use | Medium, must inform individuals but less detailed |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, specific to stated purposes | More flexible, allows broader data use if justified |
Both approaches necessitate thorough documentation and clear communication strategies. When relying on consent, organizations must make certain that it is specific, informed, and freely given. For legitimate interests, a balancing test must be conducted, weighing the organization’s needs against the potential impact on data subjects. This guarantees compliance with GDPR while leveraging AI’s capabilities responsibly and ethically.
Special Categories of Personal Data
Managing the complexities of AI data processing under GDPR, especially concerning special categories of personal data, requires additional safeguards and a lawful basis that addresses heightened privacy risks. Special categories of personal data include sensitive information such as racial or ethnic origin, political opinions, religious or philosophical beliefs, trade union membership, genetic data, biometric data for identification, health data, and data concerning a person’s sex life or sexual orientation. Given their sensitive nature, processing these data types necessitates strict adherence to GDPR provisions.
Finding a lawful basis for processing special category data is critical. Common lawful bases include:
- Explicit Consent: The data subject must give clear and explicit permission for their data to be processed.
- Employment and Social Security: Processing may be necessary for employment, social security, or social protection law.
- Public Interest: Processing may be required for reasons of substantial public interest, based on EU or member state law.
Organizations must implement robust measures to guarantee compliance with GDPR, including conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) and establishing clear protocols for processing special category data. These steps help mitigate risks and protect the privacy of individuals, fostering trust and legal compliance.
Transparency in AI Decision-Making
Transparency in AI decision-making is essential for GDPR compliance, necessitating the use of Explainable AI (XAI) techniques to clarify the logic behind automated decisions. Organizations must guarantee that users are adequately informed about how their data is processed, the purpose of the processing, and the lawful basis for it. Additionally, obtaining clear consent from users and providing them with easy access to information about AI systems enhances trust and accountability.
Explainable AI (XAI) Techniques
Explainable AI (XAI) techniques play an essential role in enhancing the transparency of AI decision-making processes, aligning with GDPR’s core principles of accountability and fairness. These techniques are designed to make AI decisions more interpretable, providing insights into how and why specific outcomes are reached. This transparency is vital for ensuring that AI systems adhere to GDPR requirements, which mandate that individuals have the right to understand the logic behind automated decisions impacting them.
XAI techniques can be categorized into several approaches:
- Post-Hoc Explanations: These methods provide explanations after the AI model has made a decision, often using tools like LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) to highlight important features influencing the outcome.
- Model Transparency: This involves designing AI models that are inherently interpretable, such as decision trees or linear models, which allow stakeholders to easily understand the decision-making process.
- Visualization Tools: These tools present complex AI decisions in a visual format, making it easier for users to grasp the rationale behind specific outcomes.
Implementing XAI techniques not only fosters trust in AI systems but also helps organizations meet GDPR compliance by ensuring that decision-making processes are transparent and understandable to data subjects.
User Notification and Consent
Ensuring that users are adequately informed about AI decision-making processes and obtaining their explicit consent is a vital component of GDPR compliance. This not only fulfills a legal obligation but also fosters trust and transparency. Users must be clearly notified about how their data will be used, the logic behind AI decisions, and the potential impact of these decisions. The GDPR mandates that consent must be specific, informed, and unambiguous, ensuring users are fully aware of what they are agreeing to.
To effectively communicate this, organizations should employ clear and accessible methods, such as privacy notices and consent forms. The following table outlines the key elements of user notification and consent:
| Aspect | Requirement | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Notification | Inform users about data collection and AI decision-making processes | Transparency about AI operations and data usage is vital. |
| Consent | Obtain explicit, informed consent | Users must clearly agree to data processing activities. |
| Purpose | Specify the purpose of data processing | Users should know the exact reasons for data collection. |
| Rights Information | Inform users of their rights under GDPR | Users should be aware of their rights to access, rectify, or erase data. |
Data Protection Strategies for AI
Implementing robust data protection strategies in AI necessitates adherence to GDPR principles such as data minimization and purpose limitation. By guaranteeing that only essential personal data is collected and processed for specific, legitimate purposes, organizations can greatly mitigate privacy risks. Additionally, incorporating privacy by design and default from the outset of AI development guarantees that data protection measures are embedded into the core of AI systems, fostering compliance and safeguarding user trust.
For a comprehensive guide on developing GDPR-compliant AI systems, including practical tips on implementing privacy by design and privacy by default principles, you can refer to this detailed resource on GDPR considerations for AI development and use.
Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
In the domain of AI development, adhering to GDPR’s principles of data minimization and purpose limitation is paramount to guarantee that only essential data is collected and utilized for clearly defined objectives. These principles are vital in safeguarding compliance and protecting individuals’ privacy in an era where AI systems increasingly rely on vast amounts of data.
Data minimization mandates that AI developers collect the minimum amount of personal data necessary for their specific purposes. This approach not only aligns with regulatory requirements but also mitigates risks associated with data breaches and misuse. Purpose limitation, on the other hand, requires that data be used exclusively for the objectives initially specified and not repurposed without proper legal basis.
Key strategies include:
- Data Inventory Management: Regularly review and update the inventory of all personal data processing activities, making sure that only essential data is retained.
- Clear Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of data collection purposes and confirm that these are communicated explicitly to data subjects.
- Data Anonymization: Where possible, anonymize data to mitigate risks and potentially exclude it from GDPR scope, while being mindful of re-identification risks.
Privacy by Design and Default
Privacy by design and default, a core principle of GDPR, necessitates the integration of data protection measures throughout the AI system development lifecycle, from initial planning to deployment and beyond. This approach mandates that privacy considerations are embedded into the fabric of AI systems, ensuring that personal data protection is not an afterthought but a foundational element.
To achieve this, AI developers must begin by conducting thorough Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) to identify potential risks to personal data early in the design phase. This proactive strategy allows for the implementation of robust safeguards tailored to the specific risks identified. Ensuring data minimization is vital, meaning only the necessary data for achieving the AI’s purpose is collected and processed, reducing exposure to potential data breaches.
In addition, AI systems should incorporate strong security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to protect personal data from unauthorized access. Regular audits and updates to the AI system are essential to maintain compliance with evolving GDPR requirements and to address any new vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, transparency must be prioritized, informing data subjects about how their data is used and their rights under GDPR. By embedding these principles, AI developers can build systems that respect privacy and comply with GDPR standards.
Conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments
Conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) is a critical step for AI projects that involve high-risk data processing activities. These assessments are necessary to identify and mitigate potential privacy risks associated with AI technologies. Key components of an AI-focused DPIA include evaluating the nature, scope, context, and purposes of data processing, as well as implementing measures to address identified risks and guarantee compliance with GDPR.
When DPIAs are Necessary for AI Projects
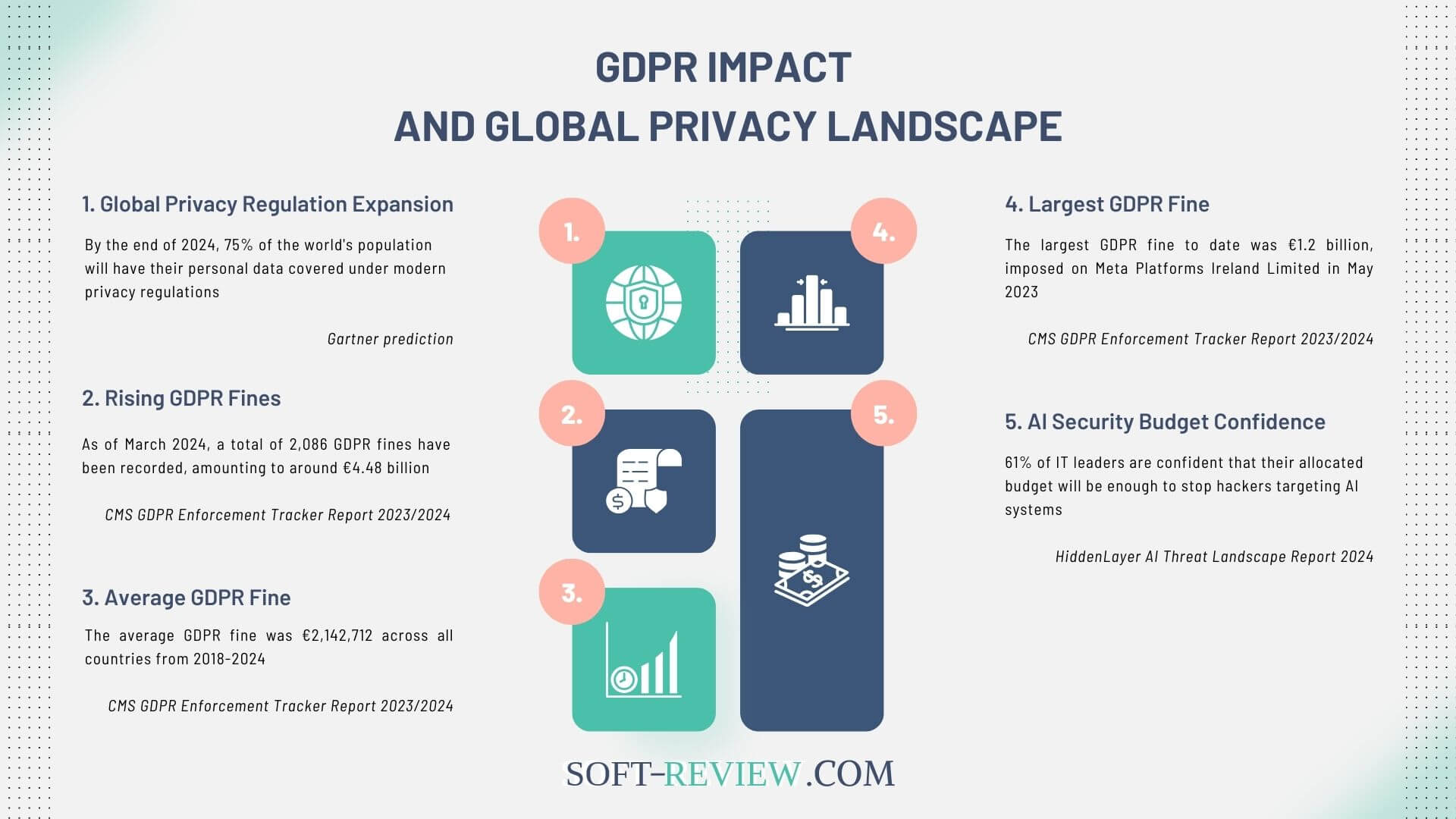
Given the potential risks associated with processing personal data, Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) are often mandated for AI projects to guarantee compliance with GDPR. DPIAs are essential in identifying and mitigating risks related to individuals’ privacy and are particularly vital for AI systems due to their complex data processing activities.
The necessity of conducting a DPIA arises in several scenarios:
- High-Risk Processing: AI projects involving large-scale processing of personal data, particularly special categories of data (e.g., health, biometric data), typically require DPIAs due to the heightened privacy risks.
- Automated Decision-Making: When AI systems make decisions that produce notable effects on individuals, such as profiling or automated decision-making processes, a DPIA is mandated to assess and mitigate potential adverse impacts.
- Innovative Technology: The use of new or emerging AI technologies that considerably impact privacy rights also necessitates a DPIA to evaluate the implications and secure compliance with GDPR principles.
Key Components of an AI-focused DPIA
Evaluating the key components of an AI-focused Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) involves a meticulous evaluation process tailored to the unique risks and nuances associated with AI technologies. Central to this process is the identification of potential high-risk data processing activities, given AI’s propensity to handle vast amounts of personal data. The initial step requires a thorough mapping of data flows, detailing how data is collected, processed, stored, and shared.
Risk evaluation is another significant component, focusing on identifying and mitigating potential privacy impacts. This includes determining the likelihood of re-identification from anonymized data, the implications of processing special categories of data, and ensuring data minimization principles are adhered to. In addition, the DPIA must address transparency and accountability, necessitating clear communication plans to inform data subjects about data processing practices and their rights.
Documenting lawful bases for processing personal data is essential, as is implementing controls to exclude special categories of data unless explicitly necessary. The findings of the DPIA should be integrated with broader AI governance frameworks, ensuring consistency in risk evaluations. Ultimately, regular reviews and updates to the DPIA are vital to address evolving risks and compliance requirements.
Individual Rights and AI
Understanding individual rights under GDPR is essential when integrating AI into data processing activities. Key rights include the right to explanation, which mandates that individuals can obtain meaningful information about the logic, significance, and consequences of automated decisions, and the right to object to automated decision-making, allowing individuals to challenge and request human intervention in such processes. Ensuring these rights are upheld requires rigorous documentation, transparency measures, and compliance protocols within AI systems.
Right to Explanation
The ‘Right to Explanation’ under the GDPR mandates that individuals receive clear, comprehensible explanations about decisions made by AI systems that affect them. This right is essential to guarantee transparency and accountability in automated decision-making processes, which can greatly impact individuals’ lives. Providing these explanations poses a unique challenge for AI developers, as the underlying algorithms are often complex and not easily interpretable.
Key elements to take into account include:
- Transparency: AI systems must be designed to provide explanations about their decision-making processes. This includes detailing how data inputs lead to specific outcomes.
- Comprehensibility: Explanations should be accessible and understandable to laypersons, avoiding overly technical jargon that may obscure the decision-making process.
- Accountability: Organizations using AI must maintain records of decision-making processes and be prepared to justify decisions if questioned by individuals or regulatory bodies.
Implementing the ‘Right to Explanation’ involves not only building technical solutions that can generate these explanations but also making certain that staff are trained to communicate effectively with affected individuals. This requirement underscores the importance of integrating ethical considerations and transparency into the AI development lifecycle, fostering trust and compliance with GDPR standards.
Right to Object to Automated Decision-Making
When individuals exercise their right to object to solely automated decision-making under the GDPR, it necessitates that AI developers implement mechanisms to guarantee human intervention in such processes. This right is particularly essential in scenarios where automated decisions greatly affect individuals, such as in credit scoring or employment assessments. To comply, AI systems must be designed to incorporate a human-in-the-loop approach, ensuring that decisions are reviewed and validated by human operators.
Moreover, developers must provide clear communication channels for individuals to express their objections. This involves not only technical adjustments but also procedural changes to facilitate prompt and effective responses to such requests. Documentation of these processes is indispensable, as it demonstrates compliance and helps mitigate legal risks.
AI developers should also conduct regular audits and evaluations of their systems to identify and rectify any biases or inaccuracies. Ensuring transparency about decision-making processes is another vital aspect, requiring that individuals are informed about how decisions are made and the criteria used. By embedding these practices, developers can better align their AI systems with GDPR requirements, thereby safeguarding individual rights and maintaining trust in automated decision-making technologies.
Handling Data Breaches in AI Systems
Handling data breaches in AI systems requires robust detection and reporting procedures tailored to the unique challenges these technologies present. Organizations must implement advanced monitoring tools to promptly identify breaches and establish clear protocols for notifying relevant authorities and affected individuals within the GDPR-mandated timeframes. Additionally, it is essential to mitigate AI-specific risks by regularly updating security measures and conducting thorough risk assessments to safeguard personal data throughout the AI lifecycle.
Detection and Reporting Procedures
Identifying data breaches in AI systems demands a robust framework that integrates advanced monitoring tools and regular audits. The complexity and scale of AI applications necessitate proactive measures to swiftly detect and address potential breaches, guaranteeing compliance with GDPR requirements.
Key components of an effective detection and reporting procedure include:
- Real-time Monitoring: Utilize AI-driven monitoring systems to continuously scrutinize data flows and detect anomalies indicative of a breach. These systems can flag unusual patterns that may signify unauthorized access or data leakage.
- Regular Audits: Conduct systematic audits of AI processes and data management practices. Regular audits help identify vulnerabilities and guarantee that all security protocols are consistently applied and updated according to the latest standards.
- Incident Response Plans: Develop extensive incident response plans that outline specific steps to be taken immediately upon detecting a breach. These plans should detail roles and responsibilities, communication strategies, and mitigation actions to minimize the impact on affected individuals and systems.
Mitigating AI-specific Risks
Mitigating AI-specific risks necessitates implementing robust security measures tailored to the unique vulnerabilities inherent in AI systems. Given that AI systems often process vast amounts of data, they are particularly susceptible to data breaches, necessitating specialized strategies to protect personal information.
First, encryption protocols should be employed to safeguard data both at rest and in transit. Effective encryption guarantees that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains unreadable and unusable. Additionally, robust access controls are imperative. Implementing role-based access and multi-factor authentication can limit data access to authorized personnel only.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are essential in identifying potential weaknesses within AI systems. These assessments should be complemented by continuous monitoring to detect anomalies or unauthorized activities in real time. In the event of a breach, predefined incident response plans must be in place, allowing for swift action to mitigate damage and comply with GDPR’s breach notification requirements.
Furthermore, anonymization techniques can be employed to reduce the risk of personal data exposure. By guaranteeing that data cannot be traced back to individuals, the severity of potential breaches can be notably minimized. Overall, a thorough, proactive approach is crucial in safeguarding AI systems against data breaches.
Compliance and Penalties
Ensuring compliance with GDPR in AI applications is paramount, as non-compliance can lead to substantial penalties, including fines of up to €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover, whichever is higher. Organizations must implement robust data protection measures, conduct regular Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), and maintain thorough documentation to mitigate risks. Proactive engagement with regulatory authorities and continuous monitoring of compliance can help avoid costly repercussions and safeguard the integrity of AI systems.
GDPR Enforcement in AI Applications
In the rapidly evolving landscape of AI, regulatory bodies are increasingly focused on enforcing GDPR compliance to protect personal data and uphold privacy standards. The intersection of AI and GDPR presents unique challenges, particularly in guaranteeing that AI applications do not infringe on individuals’ data rights. Regulatory authorities are meticulously scrutinizing AI systems to confirm they adhere to GDPR’s stringent requirements.
To navigate this complex regulatory environment, organizations must:
- Conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs): DPIAs are mandatory for high-risk data processing activities, including many AI applications, to identify and mitigate potential privacy risks.
- Maintain Transparency and Accountability: Organizations must provide clear privacy notices explaining how personal data is collected, processed, and used in AI systems, guaranteeing that data subjects are fully informed.
- Implement Robust Data Governance Frameworks: Establishing thorough data governance policies helps in managing data processing activities, guaranteeing compliance with GDPR principles such as data minimization and purpose limitation.
Potential Fines and Remediation Measures
As organizations endeavor to meet GDPR requirements within their AI applications, the potential consequences of non-compliance, including hefty fines and mandated remediation measures, underscore the importance of rigorous adherence to data protection standards. GDPR violations can lead to substantial financial penalties, with fines reaching up to €20 million or 4% of the global annual turnover, whichever is higher. These fines serve as a stark reminder of the critical need for compliance.
Beyond financial repercussions, non-compliance may result in enforced corrective actions. Organizations might be required to halt data processing activities until compliance is achieved or take specific actions to rectify identified issues. This can include conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), implementing technical and organizational measures to enhance data security, and ensuring transparent communication with data subjects.
Furthermore, regulatory authorities may mandate regular audits to monitor ongoing compliance, adding an additional layer of scrutiny. Remediation measures often involve revisiting and refining data handling practices, ensuring lawful bases for data processing, and enhancing transparency in AI operations. By proactively addressing these compliance requirements, organizations can mitigate risks and foster trust, safeguarding both their reputation and operational integrity.
Ethical Considerations in AI Development
Ethical considerations in AI development are paramount, particularly in addressing bias and discrimination while balancing innovation with privacy protection. Ensuring AI systems do not perpetuate or exacerbate existing biases requires rigorous data analysis and algorithmic transparency. In addition, developers must navigate the fine line between advancing AI capabilities and safeguarding individual privacy, adhering to GDPR principles to foster trust and maintain compliance.
For a deeper exploration of ethical considerations in AI development within the GDPR framework, you can refer to this comprehensive analysis on “GDPR and Artificial Intelligence: Challenges and Ethical Considerations”.
Addressing Bias and Discrimination
Mitigating bias and discrimination in AI development necessitates rigorous strategies to guarantee fairness and equity throughout the system lifecycle. AI systems can perpetuate or amplify biases present in training data, leading to unfair outcomes. Addressing these issues is critical to uphold ethical standards and comply with regulatory requirements like GDPR.
To effectively tackle bias and discrimination, AI developers should implement the following strategies:
- Diverse and Representative Data: Ascertain datasets used for training AI models are diverse and representative of all relevant populations to avoid skewed outcomes.
- Bias Detection Tools: Utilize specialized tools and techniques to identify and measure biases in datasets and AI models. Regularly audit these systems to monitor and mitigate potential biases.
- Inclusive Development Teams: Assemble diverse development teams to bring varied perspectives and insights, which can help identify and rectify biases during the AI development process.
Balancing Innovation and Privacy Protection
Striking a balance between advancing AI capabilities and safeguarding individual privacy requires a nuanced approach that integrates ethical principles and regulatory compliance. This balance is essential to guarantee that innovation does not come at the cost of individual rights, especially under stringent regulations like the GDPR. Key considerations include transparent data processing, the ethical use of AI, and stringent privacy protection measures.
| Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Transparency | AI systems must clearly communicate data usage and processing. |
| Data Minimization | Collect only data that is essential for the AI’s function. |
| Ethical Use of AI | Guarantee AI applications align with ethical guidelines. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhere to GDPR requirements for lawful data processing. |
Transparency is a cornerstone, as AI systems must clearly communicate how data is collected, processed, and utilized. Data minimization principles emphasize collecting only essential data to reduce privacy risks. Ethical use of AI necessitates that applications align with established ethical standards, guaranteeing fairness and mitigating biases. Regulatory compliance with GDPR involves maintaining lawful bases for data processing and conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) for high-risk activities.
The Future of AI Regulation
As AI technology continues to advance, the future of AI regulation is likely to see the introduction of AI-specific legislation aimed at addressing unique challenges posed by these systems. Global trends indicate a move towards more thorough governance frameworks, with regions like the European Union leading the charge in establishing stringent guidelines. These developments will necessitate continuous adaptation by AI developers to guarantee compliance, mitigate risks, and uphold ethical standards.
Proposed AI-Specific Legislation
Numerous jurisdictions around the globe are actively considering AI-specific regulations that aim to address the unique challenges posed by artificial intelligence technologies. The European Union, for instance, has proposed the Artificial Intelligence Act, which seeks to create a thorough legal framework for AI, focusing on risk-based regulation and guaranteeing ethical AI development. This proposed legislation underscores the need for transparency, accountability, and human oversight in AI systems.
Key elements of proposed AI-specific legislation often include:
- Risk classification: AI systems are categorized based on their risk levels, from minimal to high-risk, with corresponding regulatory requirements.
- Transparency requirements: Obligations for AI developers to disclose information about data sources, algorithms, and decision-making processes.
- Human oversight: Making certain that critical decisions made by AI systems include human intervention to prevent harm and guarantee accountability.
These legislative efforts reflect a growing recognition of the need to balance innovation with robust data protection and ethical considerations. AI developers and businesses must stay informed about these evolving regulatory landscapes to maintain compliance and foster trust in AI technologies. As these regulations take shape, they will greatly influence the future trajectory of AI development and deployment.
Global Trends in AI Governance
Building on the momentum of proposed AI-specific legislation, global trends in AI governance are shaping the future landscape of regulation and ethical standards. Nations worldwide are increasingly recognizing the necessity for robust AI frameworks, aiming to mitigate risks while fostering innovation. The European Union, with its thorough GDPR, has set a precedent, prompting other regions to develop similar regulatory structures. The EU’s forthcoming AI Act is expected to implement stringent rules based on risk assessments, potentially influencing global standards.
Meanwhile, the United States is adopting a sector-specific approach, with initiatives like the Algorithmic Accountability Act aiming to address biases and transparency in AI systems. Asian countries, including China and Japan, are also establishing guidelines to balance technological advancement with data protection. China’s Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) exemplifies a move towards tighter data governance.
International collaborations, such as the Global Partnership on AI (GPAI), are fostering cross-border dialogues to harmonize AI regulations. These efforts underscore the importance of international cooperation in addressing the complex challenges posed by AI. As these trends unfold, organizations must stay informed and adapt to evolving regulatory landscapes to guarantee compliance and ethical AI deployment.
Conclusion
Steering through the intersection of AI and GDPR requires a nuanced understanding of data protection regulations, lawful data processing, and transparency in automated decision-making. Ensuring compliance involves conducting rigorous Data Protection Impact Assessments, preparing for potential data breaches, and implementing robust risk management strategies. As AI technologies evolve, continuous attention to ethical considerations and adherence to regulatory requirements will be essential. Stakeholders must stay informed and proactive to effectively manage the complexities of AI within the regulatory framework.






